IV Ketamine Therapy
How it helps depression
Ketamine is a highly effective treatment option for individuals who have not responded well to traditional antidepressant medications or psychotherapy. If you continue to experience depressive symptoms despite trying multiple treatment options, ketamine may be a good option to consider.
One of the key benefits of ketamine is its rapid onset of action, with many patients experiencing significant improvement in symptoms within hours or days of the first infusion. This is in contrast to traditional antidepressant medications, which can take several weeks or months to take effect.
Ketamine works by blocking a neurotransmitter called glutamate in the brain, which has been linked to depression and other mood disorders. This mechanism of action is different from traditional antidepressants, which work primarily on the neurotransmitters serotonin and norepinephrine.
In addition to its rapid onset of action, ketamine has also been shown to have a sustained effect on depressive symptoms. Many patients experience relief from symptoms for several weeks to months after a course of ketamine infusions.
Furthermore, ketamine has been shown to be effective in treating a variety of depressive disorders, including major depressive disorder, bipolar depression, and postpartum depression. It has also been shown to reduce suicidal thoughts in individuals with treatment-resistant depression.
Overall, if you continue to experience depressive symptoms despite trying multiple treatment options, ketamine may be a safe and effective option to consider. However, it’s important to discuss the potential risks and benefits of ketamine treatment with your healthcare provider and work together to develop an individualized treatment plan that meets your specific needs and goals.
How it helps anxiety
Ketamine has been found to help alleviate symptoms of anxiety in a number of studies and clinical trials. It is thought to work by targeting the brain’s glutamate system, which plays a role in regulating mood and emotions. Specifically, ketamine acts as an NMDA receptor antagonist, which can lead to the release of certain neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and dopamine, that are involved in mood regulation.
Studies have shown that ketamine can produce rapid and significant reductions in symptoms of anxiety, even in people who have not responded to other treatments. The effects of ketamine typically last for several days to a week or more, and repeated treatments may provide longer-lasting relief.
It is important to note, however, that ketamine is a powerful drug with potential side effects, and should only be used under the guidance of a trained medical professional. Additionally, while ketamine can be an effective treatment for anxiety, it is not a cure and should be used as part of a broader treatment plan that may include therapy, lifestyle changes, and other medications.
How it helps Post-traumatic Stress disorder
Ketamine has been found to be an effective treatment for symptoms of PTSD (Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder) in a number of studies and clinical trials. It is thought to work by targeting certain brain pathways and neurotransmitters that are involved in the development and maintenance of PTSD symptoms.
Specifically, ketamine can help to increase the production of certain proteins in the brain that are involved in the growth and repair of neural connections. This can help to strengthen the connections between different areas of the brain that are involved in processing and regulating emotions and memories, which can lead to a reduction in symptoms of PTSD.
Studies have shown that ketamine can produce rapid and significant reductions in symptoms of PTSD, including flashbacks, anxiety, and depression. The effects of ketamine typically last for several days to a week or more, and repeated treatments may provide longer-lasting relief.
However, it is important to note that ketamine is a powerful drug with potential side effects, and should only be used under the guidance of a trained medical professional. Additionally, while ketamine can be an effective treatment for PTSD, it is not a cure and should be used as part of a broader treatment plan that may include therapy, lifestyle changes, and other medications.
how ketamine is given
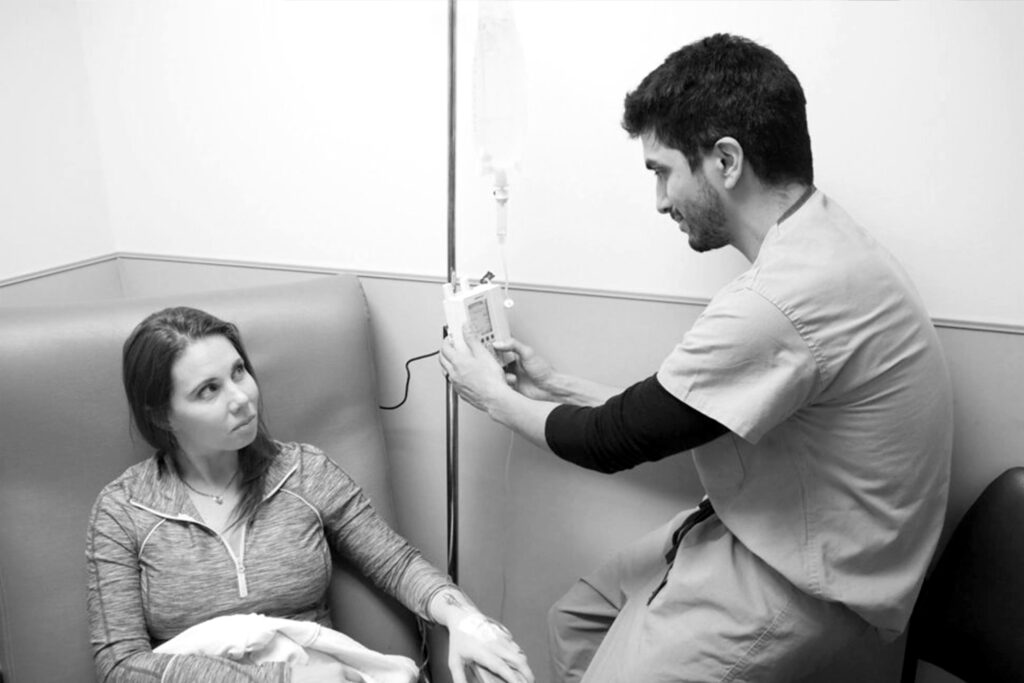
IV (intravenous) ketamine is typically given as a slow infusion through a vein in the arm or hand. The dose and rate of infusion depend on the medical condition being treated and the patient’s individual needs.
In a medical setting, a healthcare professional such as a doctor or nurse will administer IV ketamine. The patient is usually monitored closely during the infusion to ensure their safety and to adjust the dose as needed. The length of the infusion may also vary depending on the medical condition being treated, but it can range from several minutes to several hours.
It’s important to note that IV ketamine should only be administered under the guidance and supervision of a trained healthcare professional. Misuse or abuse of ketamine can have serious consequences and should be avoided.
Working together to help you seize life's events
We Want You To Be Ready For Wherever Your Next Adventure Takes You
Schedule AppointmentOffice Hours
Mon - Thu (8AM-12PM / 1-5PM) Fri (8AM-12PM)
682-285-1044
Need help? Call us today!
Get Help Today
Call Us: 682-285-1044 **
** Hours: Mon - Thu (8AM-12PM / 1-5PM) Fri (8AM-12PM)
Email Us
Book Appointment
Accepted Insurances
Our Location
120 St Louis Ave.
Suite #100
Fort Worth, Texas 76104
Our Hours
Mon - Thu (8AM-12PM / 1-5PM)
Mon - Thu (Close from 12PM to 1PM)
Fri (8AM-12PM)
Office Information
Call Us: 682-285-1044 **
** Hours: Mon - Thu (8AM-12PM / 1-5PM) Fri (8AM-12PM)
Our Location
120 St Louis Ave.
Suite #100
Fort Worth, Texas 76104
Accepted Insurances
Email Us
Book Appointment
Pain Clinic Services
Call Us: 682-285-1044 **
** Hours: Mon - Thu (8-12PM / 1-5PM) Fri (8-12PM)
1. Pain Interventions
Dr. Martinez is a pain management specialist with extensive experience in minimally invasive injections, epidural steroid injections, interventions, and infusions.
2. Ketamine Infusions
Ketamine infusions work differently than other medications to manage chronic pain. These infusion treatments help to reverse sensitization and reset receptors to help you overcome your pain.
3. Osteopathic Manipulative Medicine
Dr. Martinez is a spine and back specialist with more than 10 years of experience with adjusting joint pain and dysfunction through manipulative medicine.
4. Physical Therapy
Physical Therapy can be an essential part of addressing chronic pain of the neck, back and spine.
5. Pain Medication Management
As a pain management specialist, Dr. Martinez uses a wide variety of techniques to alleviate pain. These techniques include adjuvant medications, psychotherapy, physical therapy, surgical consultation or injections or infusions.
6. Lifestyle Management
Sometimes the first step to treating spine pain is focusing on overall lifestyle improvement. This may include nutrition, activity, exploration, socialization, introspection and more.
Email Us
Book Appointment
Accepted Insurances
Our Location
120 St Louis Ave.
Suite #100
Fort Worth, Texas 76104
Our Hours
Mon - Thu (8AM-12PM / 1-5PM)
Mon - Thu (Close from 12PM to 1PM)
Fri (8AM-12PM)
Patient Portal
Call Us: 682-285-1044 **
** Hours: Mon - Thu (8-12PM / 1-5PM) Fri (8-12PM)
Access our patient portal
To access this please click on the button below.
Accepted Insurances
Book Appointment
Email Us
Our Hours
Mon - Thu (8AM-12PM / 1-5PM)
Mon - Thu (Close from 12PM to 1PM)
Fri (8AM-12PM)
Accepted Insurances
Our Current Insurances *
* NOTE: Please call to double check with our staff.
Aetna Commercial
Aetna Medicare PPO & HMO
Aetna Texas Health EPO
BCBS TX Essentials HMO
BCBS TX High Perform Network
BCBS TX Medicare HMO
BCBS TX Medicare PPO
BCBS TX PPO/POS
BCBS TX Premier HMO
Blue Advantage HMO Exchange
Cigna
Cigna Medicare Adv.
Coventry
First Health
Friday Health Plan
Galaxy Health Network
Healthcare Highways
HealthSmart Accel
HealthSmart PPO/HPO
Humana Choice Care
Humana Medicare HMO
Humana Medicare PPO/PFFS
Imagine Health
IMS PPO
UHC Medicare Adv
UHC DIRECT
United Healthcare
